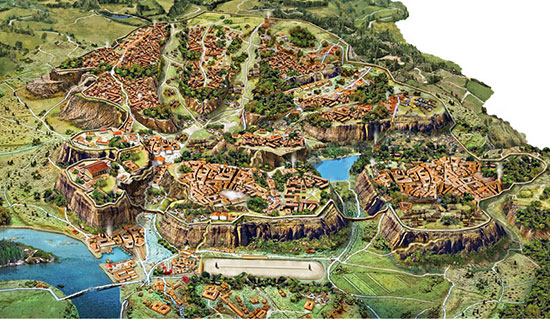
The 7 Hills of Rome
The Seven Hills of Rome are a group of hills that played a significant role in the historical and cultural development of the city. These hills are traditionally listed as follows:
- Palatine Hill:
- Location: This is the most central of the seven hills and is situated between the Roman Forum and the Circus Maximus.
- Historical Significance: The Palatine Hill is considered the center of ancient Rome and is associated with the city’s foundation myth. According to legend, it was on this hill that Romulus founded Rome in 753 BCE.
- Capitoline Hill (Capitolium):
- Location: Located between the Roman Forum and the Campus Martius, the Capitoline Hill is the smallest of the seven hills.
- Historical Significance: It is home to the Capitoline Museums and the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus, one of the most important temples in ancient Rome. The hill also housed important religious and civic buildings.
- Quirinal Hill:
- Location: This hill is the highest of the seven and is situated to the northeast of the Roman Forum.
- Historical Significance: The Quirinal Palace, which serves as the official residence of the President of the Italian Republic, is located on this hill. In ancient times, it was associated with the Sabines and later became a residential area for the Roman elite.
- Viminal Hill:
- Location: The Viminal Hill is situated between the Quirinal Hill and the Esquiline Hill, forming part of the northeastern boundary of ancient Rome.
- Historical Significance: It was not as significant in terms of historical monuments, but it housed various residential buildings and infrastructure.
- Esquiline Hill:
- Location: Located to the northeast of the Roman Forum, the Esquiline Hill is one of the largest and most populous of the seven hills.
- Historical Significance: The Baths of Trajan and the House of Augustus are located on this hill. In ancient times, it was a residential area and home to some of Rome’s wealthier citizens.
- Caelian Hill:
- Location: To the southeast of the Roman Forum, the Caelian Hill is one of the quieter and more residential hills.
- Historical Significance: The Baths of Caracalla, one of the largest public baths in ancient Rome, are located on the Caelian Hill. It was also home to various Roman aristocrats.
- Aventine Hill:
- Location: Situated to the southwest of the Roman Forum, the Aventine Hill overlooks the Tiber River.
- Historical Significance: The Aventine is associated with the plebeians and was the location of several important religious sites, including the Temple of Diana and the Temple of Ceres. Today, it is a peaceful residential area.
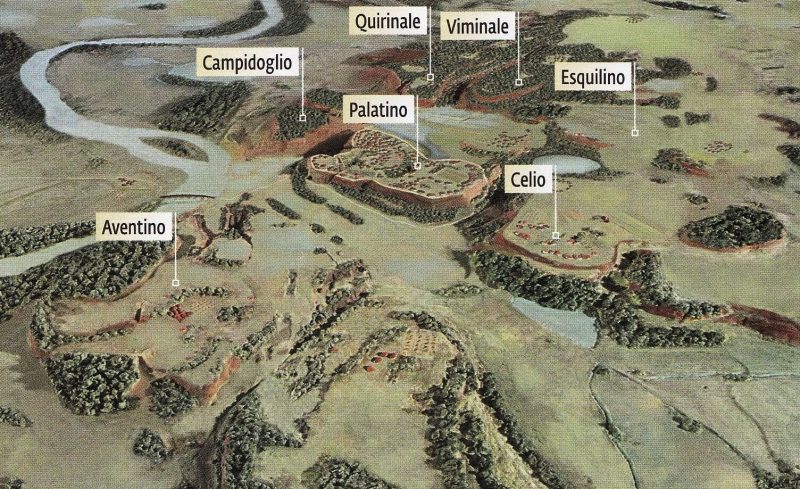
These Seven Hills of Rome played a crucial role in shaping the city’s geography, culture, and history, and their significance is deeply embedded in the foundation and growth of ancient Rome.
![]()




